scjson
| Contents | Overview | Examples | Editor | Forum | |—|—|—|—|—|
SCXML Tutorial
This project is an attempt to illustrate the current SCXML standard
New! Video version of the tutorial
Hello world

<scxml name="Scxml" version="1.0" xmlns="http://www.w3.org/2005/07/scxml">
<final id="Final">
<onentry>
<log expr="Hello, world!" label="INFO"/>
</onentry>
</final>
</scxml>
Questions & Answers
Table of contents
- Core Constructs
- Executable Content
- Data Model and Data Manipulation
- External Communications
SCXML Frameworks W3C Standard Specification Compliance
| Framework | Datamodel | W3C Mandatory | W3C Optional | Compliance |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| uSCXML 2.0 | ecmascript | 159 of 159 | 33 of 33 | Full |
| Qt SCXML 5.15 | ecmascript | 141 of 159 | 17 of 33 | Partial |
| SCION CLI 1.0.37 | ecmascript | 156 of 159 | 18 of 33 | Partial |
| PyBlendSCXML 1.0.0 | python | 159 of 159 | 22 of 33 | Partial |
Examples
2. Microwave owen (using parallel)
4. Salus RT500 (Digital Room Thermostat) Simulator
7. Infotainment Radio Bolero Simulator

Qt SCXML Examples
Articles
1. Inheritance (Visual) in SCXML (State Machines)
W3C Examples
W3C IRP tests
Donations
When we started the project in 2016 there were no SCXML illustrations, no simple explanation of SCXML details, no good examples. We felt the power of SCXML but understood that without simple explanations, illustrative examples and convinient modelling tools it’s worth nothing.
If you are interested in the development of SCXML tutorials and examples we would be highly appreciated for any help.
| Paypal |
|---|
 |
SCXML Overview
Basic State Machine Notation
The most basic state machine concepts are <state>, <transition> and event. Each state contains a set of transitions that define how it reacts to events. Events can be generated by the state machine itself or by external entities. In a traditional state machine, the machine is always in a single state. This state is called the active state. When an event occurs, the state machine checks the transitions that are defined in the active state. If it finds one that matches the event, it moves from the active state to the state specified by the transition (called the “target” of the transition.) Thus the target state becomes the new active state.

<scxml initial="Start" name="Scxml" version="1.0" xmlns="http://www.w3.org/2005/07/scxml">
<final id="Final">
<onentry>
<log expr="Finished!" label="INFO"/>
</onentry>
</final>
<state id="Start">
<transition event="Event" target="Final"/>
</state>
</scxml>
Atomic state
Does not contain any child states

<scxml name="Scxml" version="1.0" xmlns="http://www.w3.org/2005/07/scxml">
<state id="Level 1"/>
</scxml>
Compound states
May contain nested <state> elements and the nesting may proceed to any depth

<scxml name="Scxml" version="1.0" xmlns="http://www.w3.org/2005/07/scxml">
<state id="Level 1">
<state id="Level 2">
<state id="Level 3"/>
</state>
</state>
</scxml>
Parallel states
The <parallel> element represents a state whose children are executed in parallel.

<scxml name="Scxml" version="1.0" xmlns="http://www.w3.org/2005/07/scxml">
<parallel id="Airplane_Engines">
<state id="Engine_1" initial="Engine_1_Off">
<state id="Engine_1_Off">
<transition event="Start.1" target="Engine_1_On"/>
</state>
<state id="Engine_1_On">
<transition event="Shutdown.1" target="Engine_1_Off"/>
</state>
</state>
<state id="Engine_2" initial="Engine_2_Off">
<state id="Engine_2_Off">
<transition event="Start.2" target="Engine_2_On"/>
</state>
<state id="Engine_2_On">
<transition event="Shutdown.2" target="Engine_2_Off"/>
</state>
</state>
</parallel>
</scxml>
Initial state
Represents the default initial state for a complex <state> element

<scxml name="Scxml" version="1.0" xmlns="http://www.w3.org/2005/07/scxml">
<state id="Work">
<initial>
<transition target="Ready"/>
</initial>
<state id="Ready"/>
</state>
</scxml>
Final state
Represents a final state of an <scxml> or compound <state> element.

<scxml name="Scxml" version="1.0" xmlns="http://www.w3.org/2005/07/scxml">
<state id="Work">
<transition event="done.state.Work" target="WorkFinished"/>
<state id="CompletingTask">
<transition target="Completed"/>
</state>
<final id="Completed"/>
</state>
<final id="WorkFinished"/>
</scxml>
History state
The <history> pseudo-state allows a state machine to remember its state configuration. A <transition> taking the <history> state as its target will return the state machine to this recorded configuration.

<scxml name="Scxml" version="1.0" xmlns="http://www.w3.org/2005/07/scxml">
<state id="Work">
<transition event="Pause" target="Expecting"/>
<state id="Off">
<transition event="Switch" target="On"/>
</state>
<state id="On">
<transition event="Switch" target="Off"/>
</state>
<initial>
<transition target="HistoryPoint"/>
</initial>
<history id="HistoryPoint">
<transition target="Off"/>
</history>
</state>
<state id="Expecting">
<transition event="Resume" target="HistoryPoint"/>
</state>
</scxml>
Transitions
Transitions between states are triggered by events and conditionalized via guard conditions. They may contain executable content, which is executed when the transition is taken.

<scxml datamodel="lua" name="Scxml" version="1.0" xmlns="http://www.w3.org/2005/07/scxml">
<state id="Work" initial="Off">
<transition event="Update" type="internal">
<log expr="'Updated'" label="OnUpdate"/>
</transition>
<transition event="ReInit" target="Work" type="internal"/>
<transition event="Quit" target="End"/>
<transition event="error.*" target="Fail"/>
<state id="Off">
<transition cond="_event.data==1" event="Switch" target="On"/>
</state>
<state id="On">
<transition cond="_event.data==0" event="Switch" target="Off"/>
</state>
</state>
<final id="End"/>
<final id="Fail"/>
</scxml>
Invoke
SCXML provides an element <invoke> which can create external services. For example: it can create instances of external state machines
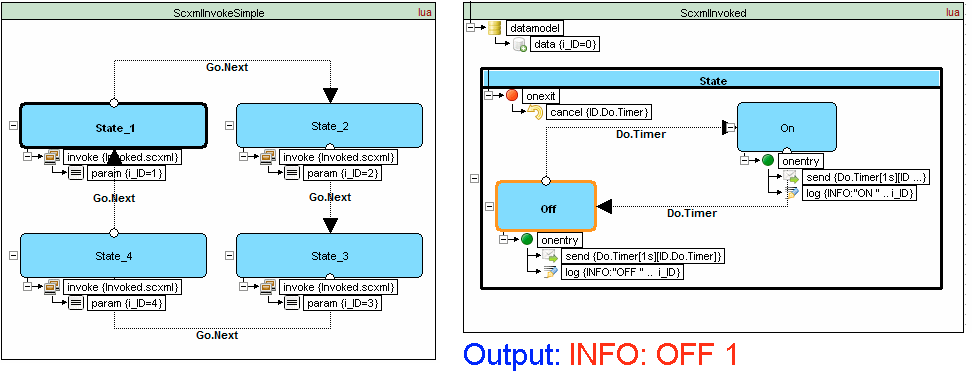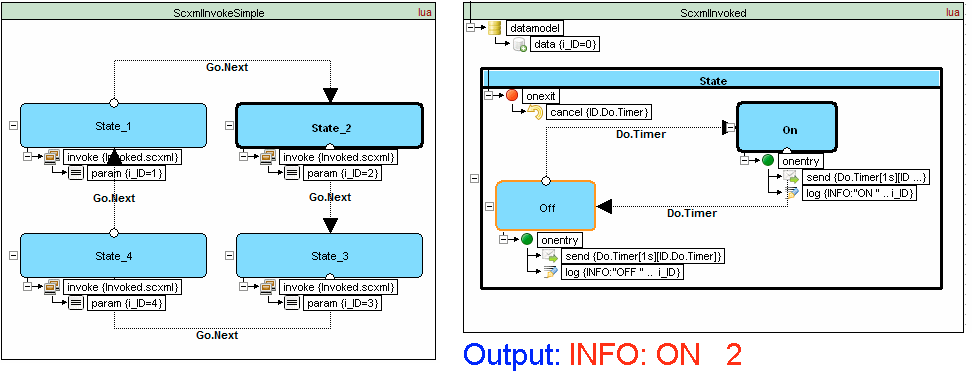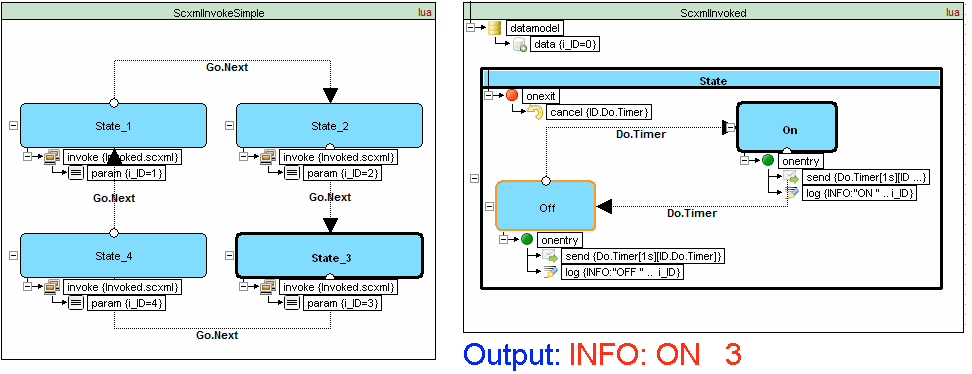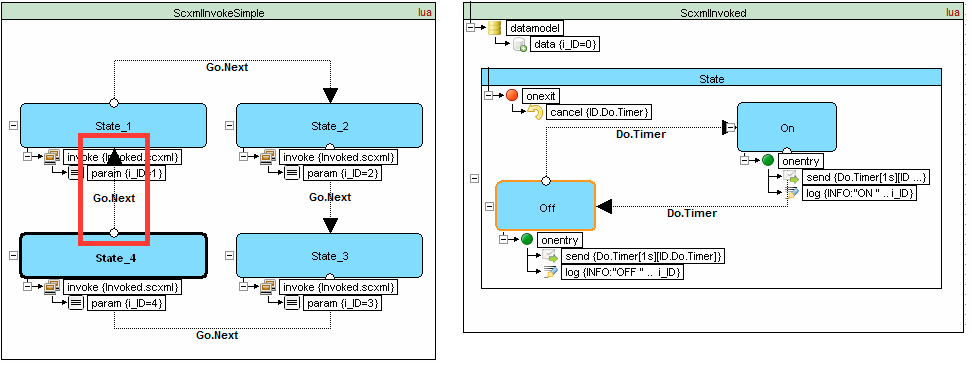
Traffic light example
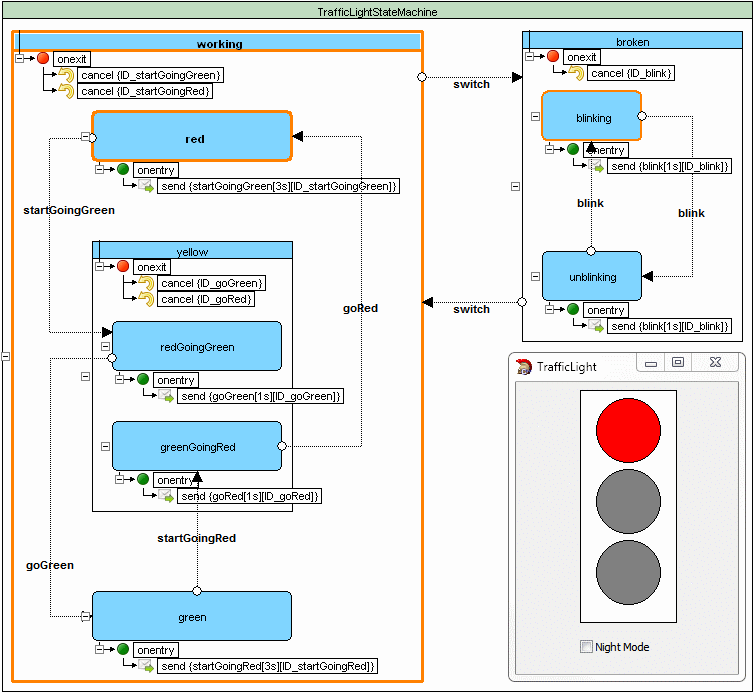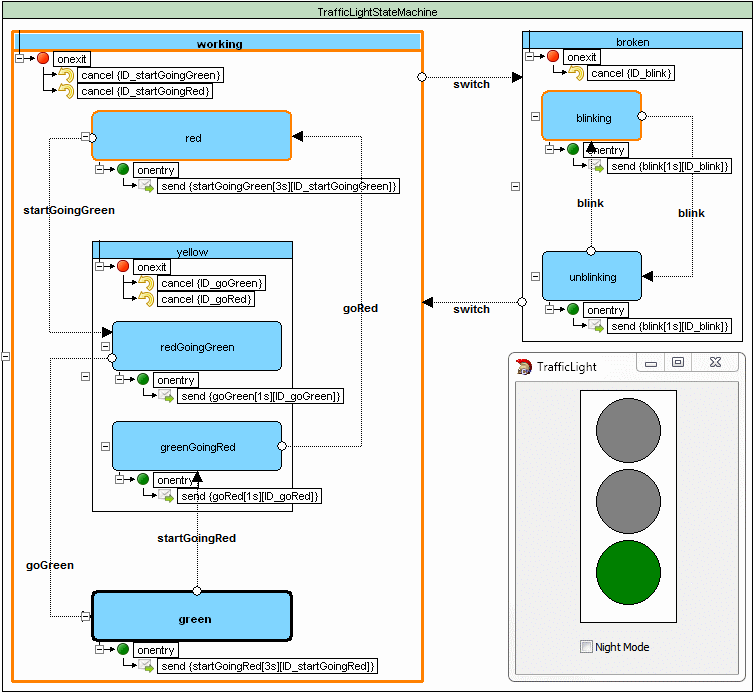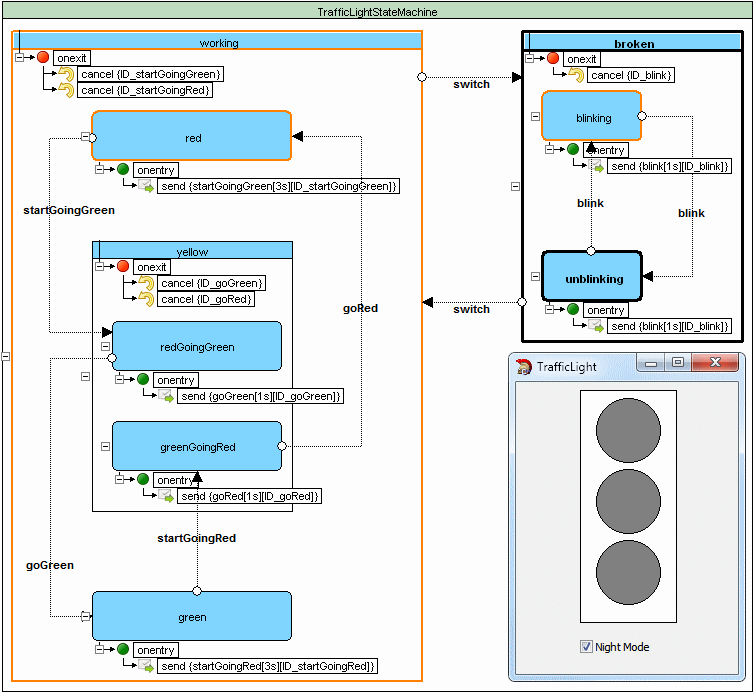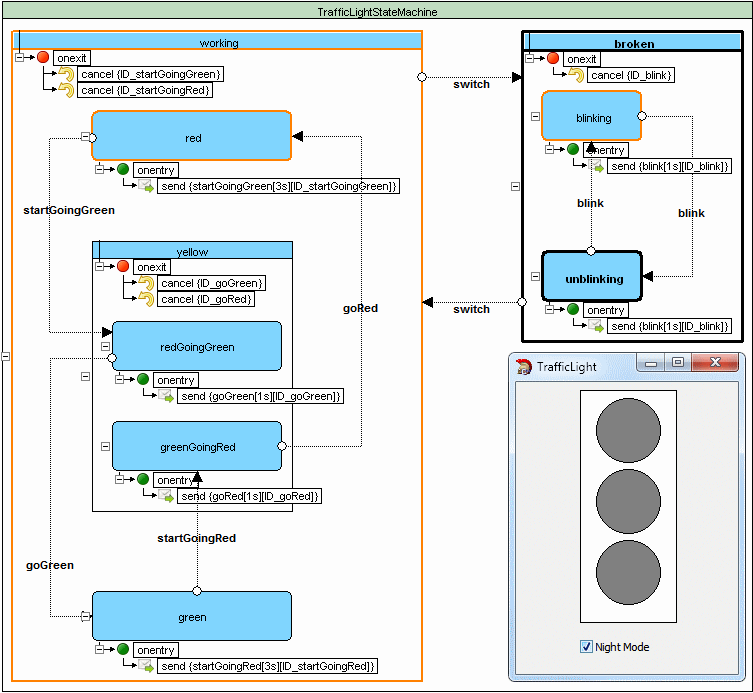
Source code
```xml
Time generator example
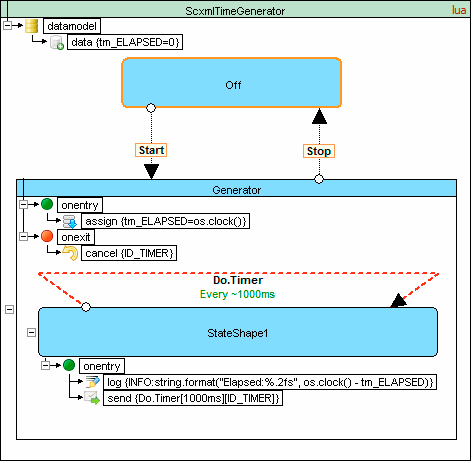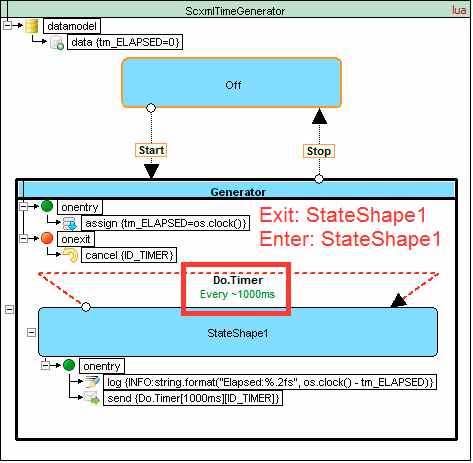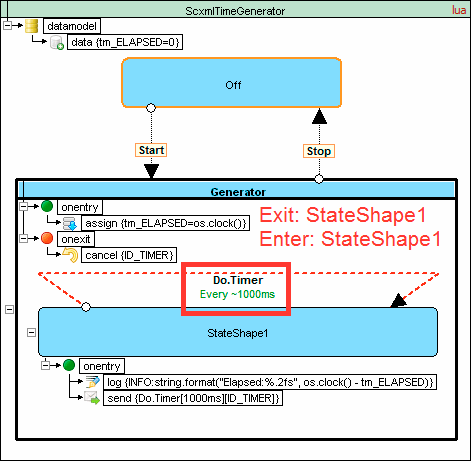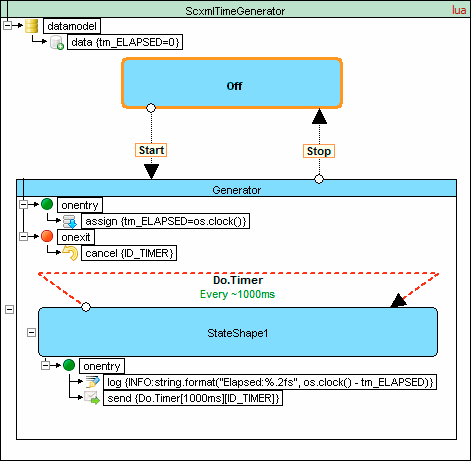
Source code
```xml
StopWatch example
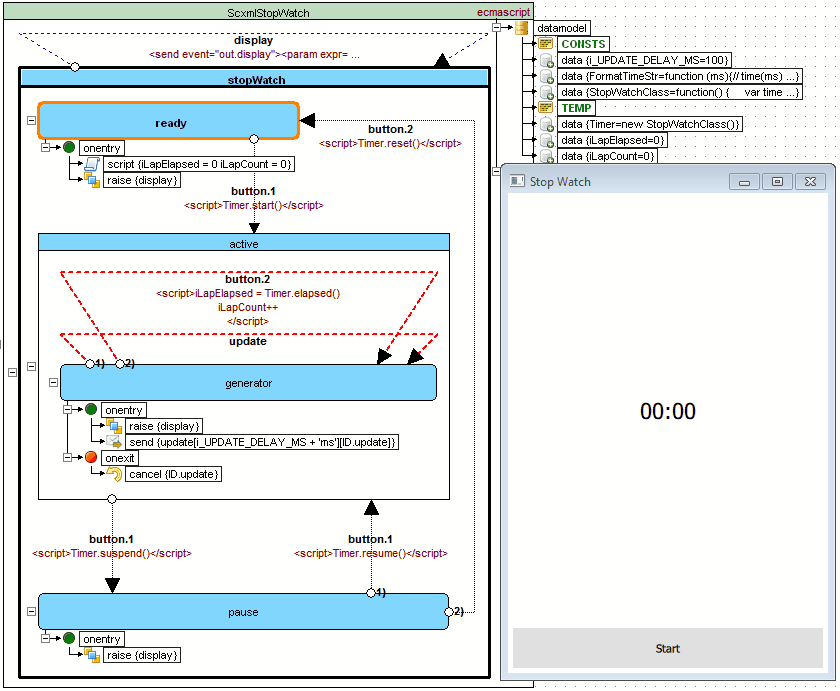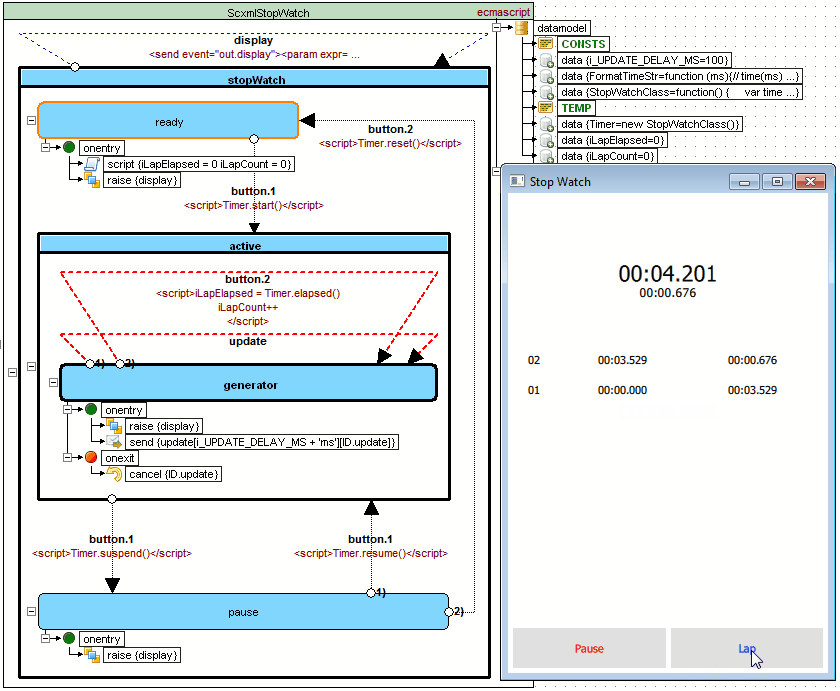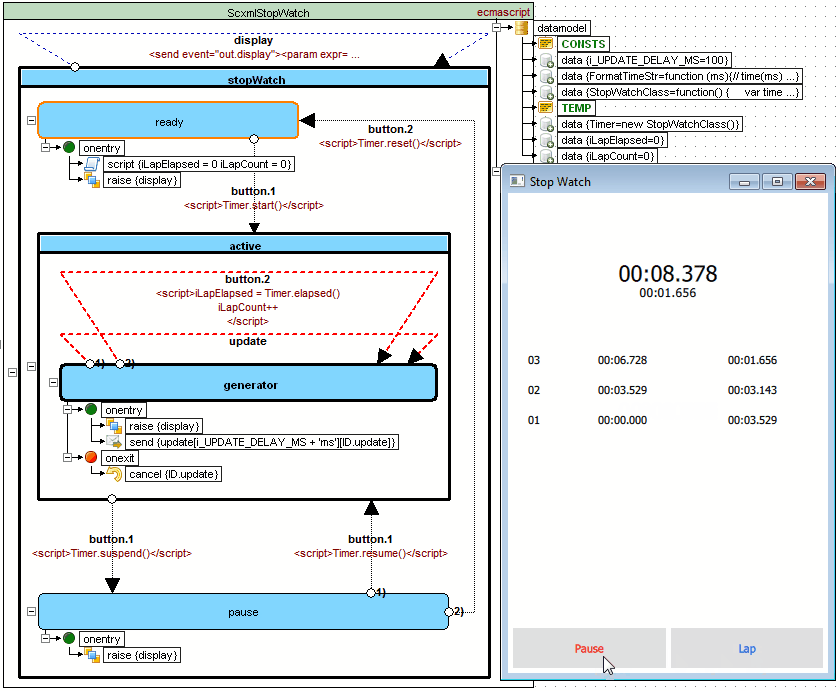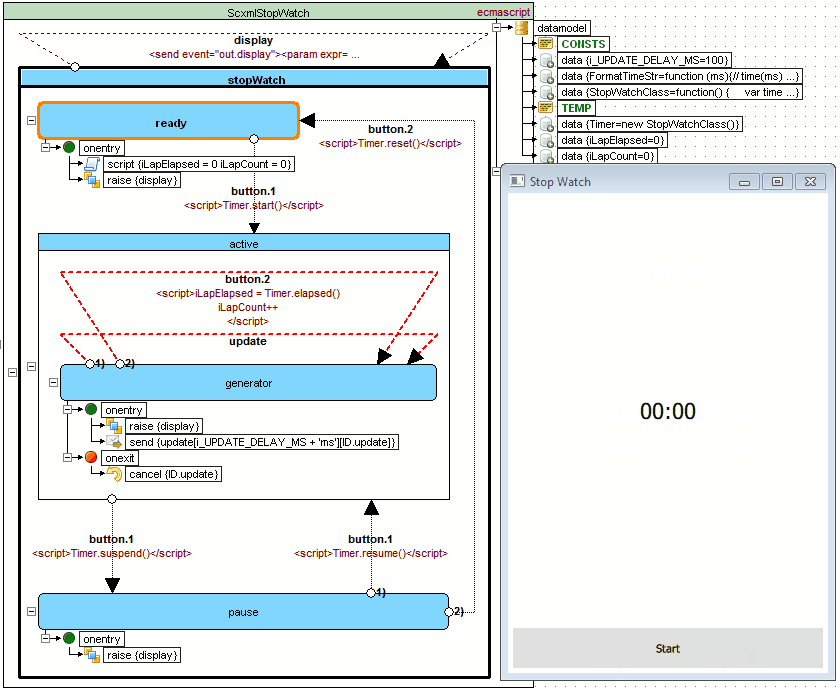
Source code
```xml
Qt Bug Tracking Workflow example
![]()
Source code
```xml
Microwave owen example

Source code
```xml
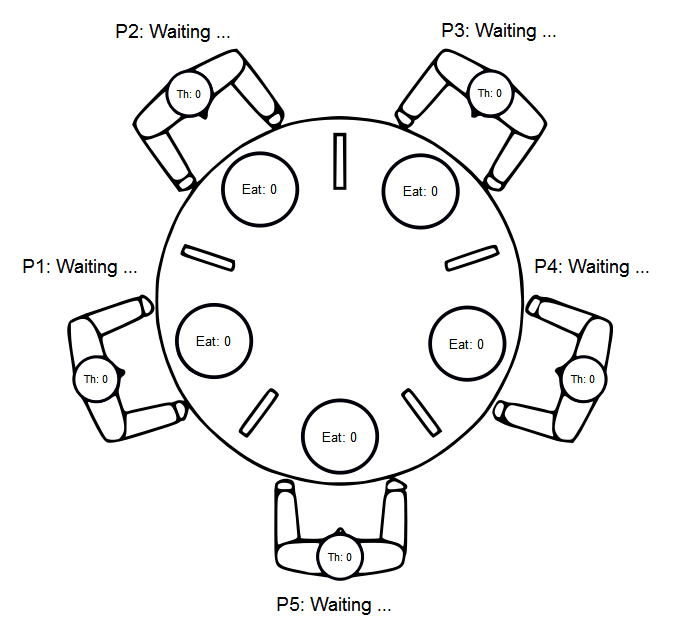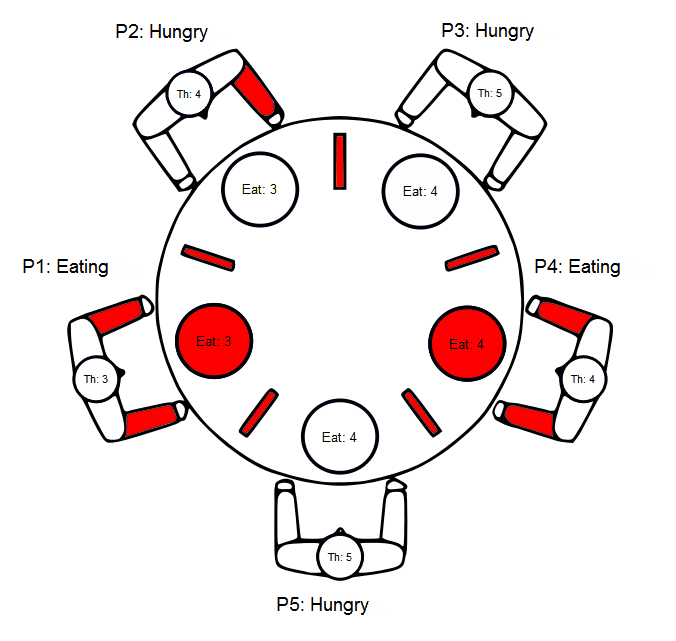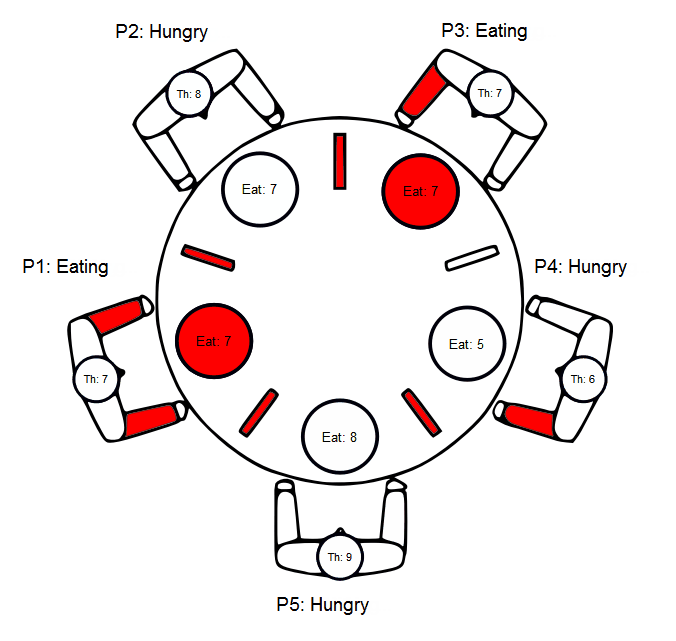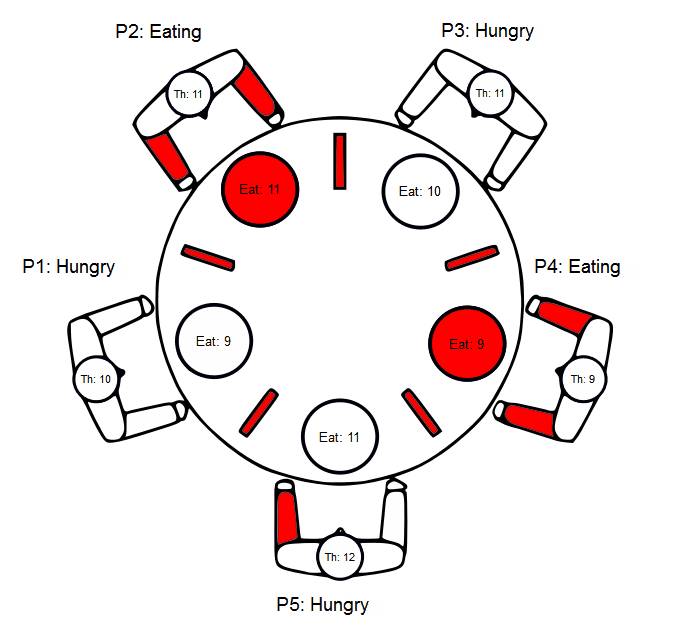
Dining Philosophers Problem example
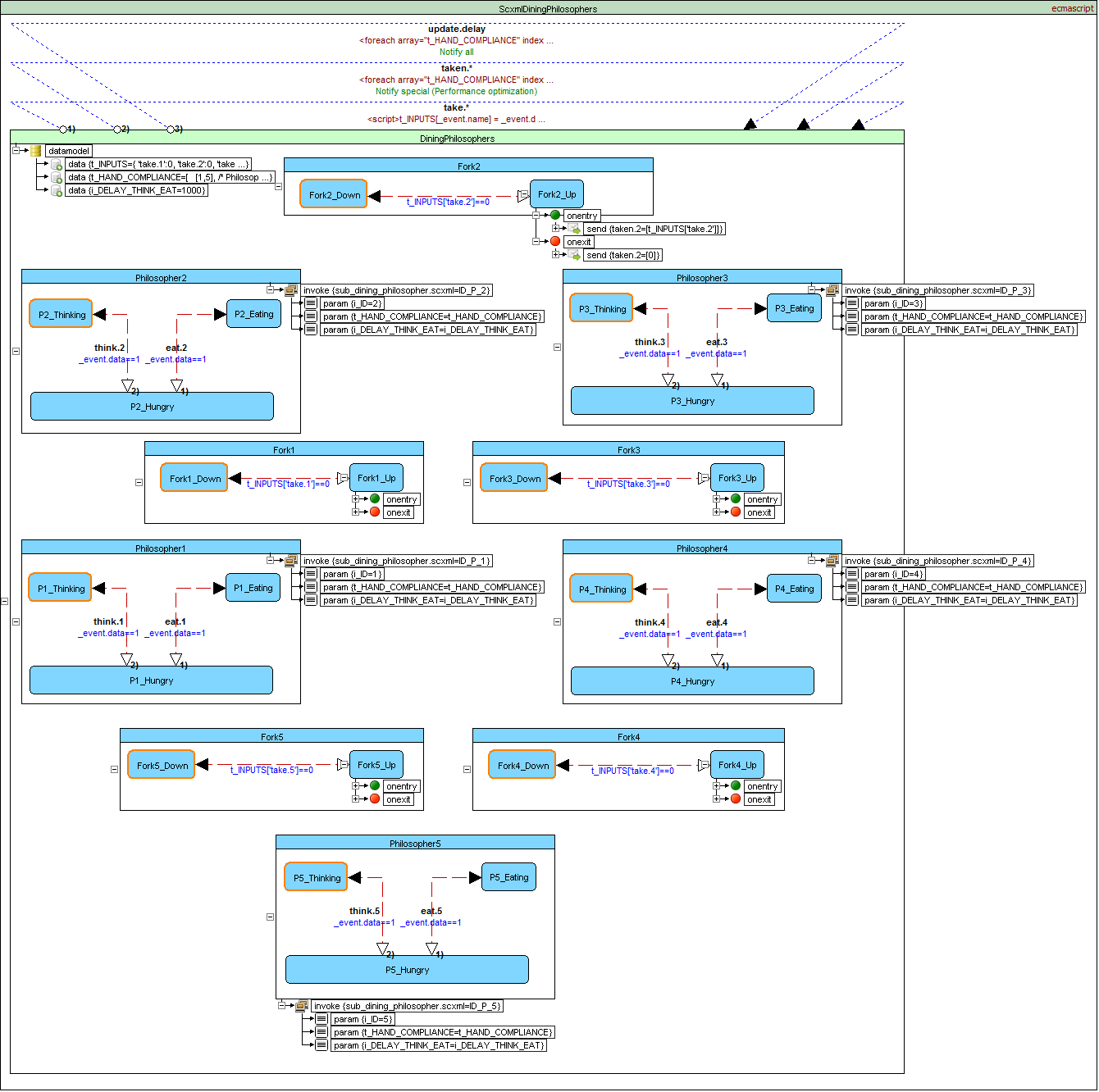
Source code - main.scxml
```xml
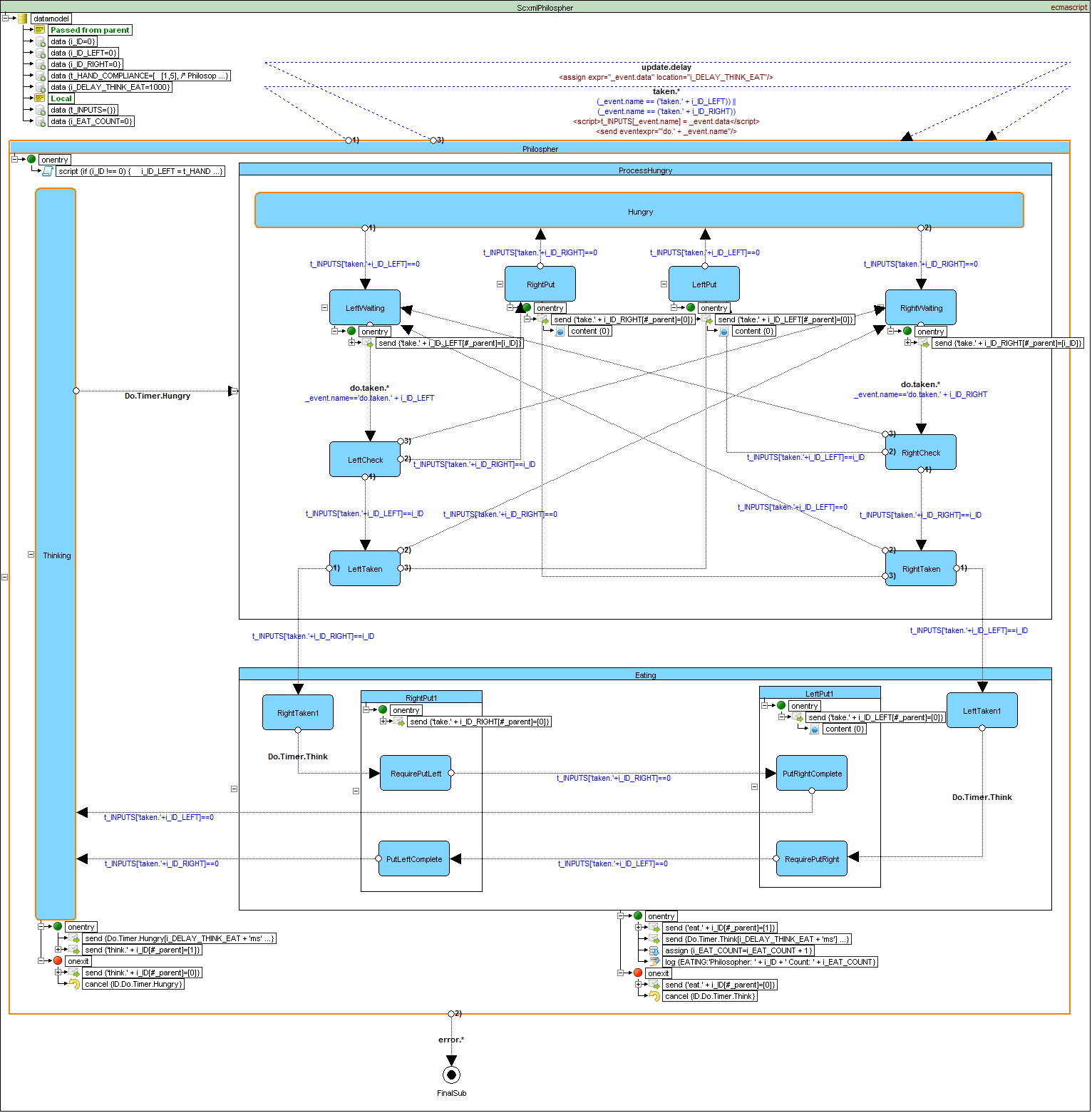
Source code - invoked.scxml
```xml
| TOP | Contents | Overview | Examples | Editor | Forum | |—|—|—|—|—|—|